Leasing is an option for individuals or businesses who are not able to pay for the purchase of a property but want the benefits of having the asset.
This lease can be of two types: 1. Financial Lease or capital lease 2. Operating Lease
Operating leases allow an individual to make monthly payments rather than one large upfront payment, and they typically run for a shorter period. Finance leases require payments to be made during both the lease period and after the lease term has ended, and they often run for a longer period.
In this article, we will describe the core difference between finance lease and operating lease, what is the effect on the balance of both leases and what should we choose between a finance lease and an operating lease.
Difference between Finance Lease and Operating Lease
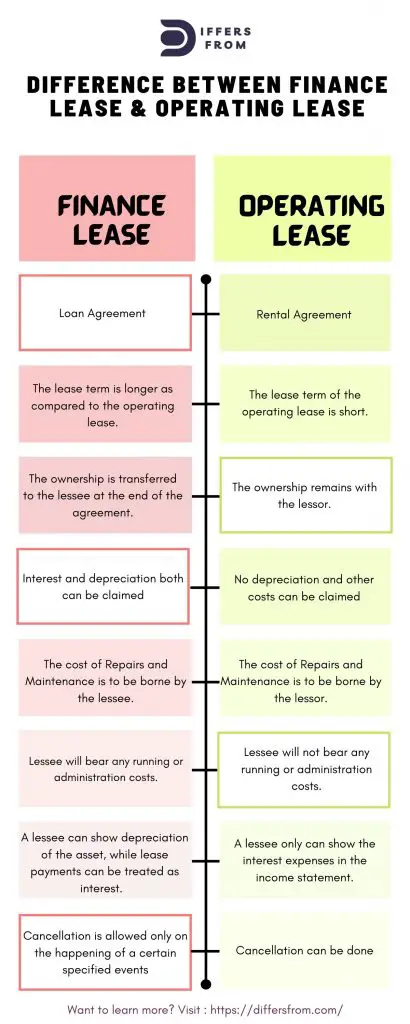
| Finance Lease | Operating License | |
| Meaning | A finance lease is basically borrowing money for purchasing assets and the borrower will pay a rental amount for a specific period of time with interest. | An operating lease is a contract wherein the owner permits the user to use an asset for a particular period that is shorter than the economic life of the asset without any transfer of ownership rights. |
| Nature | Loan Agreement | Rental Agreement |
| Lease Term | The lease term is longer as compared to the operating lease. | The lease term of the operating lease is short. |
| Transferability | The ownership is transferred to the lessee at the end of the agreement. | The ownership remains with the lessor. |
| Tax Benefit | Interest and depreciation both can be claimed | No depreciation and other costs can be claimed |
| Cost of Repairs and Maintenance | Are to be borne by the lessee. | Are borne by the lessor. |
| Running Cost | In a financial lease, the lessee will bear all the running costs and administration expenses | In an operating lease, Lessee will not bear any running or administration costs. |
| Balance Sheet Treatment | A lessee can show depreciation of the asset, while lease payments can be treated as interest. | A lessee only can show the interest expenses in the income statement. |
| Purchasing option | In a financial lease, the lessee gets an option to purchase the asset he has taken on a lease. | In an operating lease, the lessee is not given any such option. |
| Risk of obsolescence | Lies with the lessee | Lies with the lessor |
| Cancellation of the lease | Only on the happening of a certain specified event. | Can be done |
Finance Lease Vs Operating Lease: The Key Differences
- A financial lease is a sort of lease in which the lessor enables the lessee to utilize the lessor’s asset for a prolonged length of time instead of making periodic payments. In contrast, an operating lease is a type of lease in which the lessor enables the lessee to utilize the lessor’s asset in exchange for a monthly payment for a limited time.
- A financial lease is one that must be recorded in a financial accounting system. The operating lease, on the other hand, is a notion that does not require any accounting system to be recorded; this is why it is also known as an “off the balance sheet lease.”
- Under a financial lease, the lessee gains ownership of the property. The lessee does not acquire ownership of the property under an operating lease.
- A loan agreement/contract is the document that governs a financial lease. A rent agreement/contract is the contract that governs an operational lease.
- Financial leases are typically non-cancelable after both parties sign the agreement. The operational lease can be canceled only during the first time, even if the two parties have reached an agreement.
- A tax benefit for depreciation and finance expenses is available with a financial lease. Rent payments are tax-deductible under the operating lease.
- At the end of the contractual time, there is an asset purchase option in a financial lease. There is no such offer under an operational lease.
Difference between capital lease and operating lease in infographic
What is a finance lease/ Capital Lease?
A finance lease is an agreement between the lessor and the lessee in which the lessor is the legal owner of an asset and the lessee rents the asset for an agreed-upon period of time in exchange for rental payment.
After signing the agreement, a lessee has operating control over the asset. Along with this, all risks and rewards associated with the ownership of the asset are also transferred to the lessee.
Finance Lease also provides the lessee economic characters of ownership of the asset for accounting purposes.
The lessee will record the asset as a fixed asset in their balance sheet and entry the interest of the lease as an expense in the income statement.
What qualifies as a finance lease or capital lease?
To be classified as a finance lease under US GAAP, the rental agreement must have at least one of the following requirements:
- The lease rentals have a present value that is equal to or greater than the asset’s fair market value.
- The lease period is greater than 75% of the useful life of the leased item.
- The lessee is offered the opportunity to acquire the leased asset at a lower price than the fair value of the leased item.
- At the end of the lease, the lessor relinquishes legal ownership of the leased asset to the lessee.
In IFRS, however, a lease is classified as a finance lease if all of the following basic criteria are met:
- The lessor remains the legal owner of the asset
- But the risk and rewards related to leased assets are transferred to the lessee
- And after the end of the lease, legal ownership of the asset transfers from the lessor to the lessee.
What are the advantages of Finance Lease (Capital Lease)
- Ownership benefit:
In the Financial lease agreement, at the end of the lease, the lessee has options to buy the leased asset. Moreover, the lessee may get the purchased asset if the asset is used for more than 75% of its life.
- Claim to depreciation:
The lessee can record the leased asset on the balance sheet and claim the depreciation of the asset. Depreciation of an asset is an expense. Due to this, the company can treat this as an expense on the income statement which reduces the profit of the lessee’s company
- Claim to interest expense:
The lessee pays interest monthly or quarterly. Hence, the lessee can treat these interest expenses on the income statement. This would eventually reduce the profit and get tax benefits
- Cheaper:
Compared to other financings, leasing is generally less expensive. Besides, the lessee makes the payments over a number of years.
What are disadvantages of Finance Lease (Capital Lease)
- Negative debt-to-equity ratio:
When a lessee signs a capital lease, he adds debt to his balance sheet that must be paid back through lease payments. The lessee’s balance sheet debt to equity ratio rises as a result.
- Risk of becoming obsolete:
This would make it harder for the lessee to acquire money in the future. The lessee has the option of obtaining ownership rights. What if the leased item becomes obsolete at the conclusion of the eligibility period for ownership? As we live in a constantly changing technology world, this is frequently the case. As a result, there’s a good possibility the lessee will be left with outmoded assets for the duration of the lease.
- Maintenance Responsibilities:
During the lease period, the lessee is responsible for all repairs and maintenance of the asset. Regular maintenance expenses, insurance charges, downtime costs, repairs, and so forth are all examples of maintenance costs. If you’re unlucky, the maintenance costs might skyrocket if you have an accident or something else goes wrong.
Examples of Finance Lease:
Finance leases are used in a wide range of sectors and are typically utilized when a firm needs an expensive piece of equipment but wants to keep its cash flow and avoid paying a huge lump payment for it.
- Aircraft
- Land
- Buildings
- Plant equipment
- Heavy machinery
- Ships
What is an operating lease?
An operating lease is a contract between the owner of the asset (the lessor) and the user (the lessee) where the term of the lease is shorter than the actual useful life of the machinery or equipment.
According to Investopedia, Off-balance-sheet financing is referred to as operating leases. This implies that a leased asset and its related liabilities (for example, future rent payments) are not reflected on the balance sheet of a firm. Operating leases have historically allowed American businesses to avoid recording billions of dollars in assets and liabilities on their balance sheets, lowering their debt-to-equity ratios.
The lessee is obliged to pay regular rental or lease installments in return for using the asset for an agreed period of time. If the lessee failed to do so, the lessor can take back the asset and end the contract.
It is also to be noted that there will not be any transfer of ownership like a financial lease.
This type of contact can be beneficial for both parties. In the eye of the lessor, an operating lease provides a mechanism to earn a fixed interest on an asset. It may otherwise depreciate day by day and the owner also cannot get any return from the asset.
In the case of the Lessee, it provides a mechanism to utilize an asset or equipment without actually buying it and pay a bulk amount of money. Total payment is also less than the purchasing price of the equipment from the market.
Example of Operating Lease:
For example, a rice mill with an economic life of 10 years may be leased to a business for 8 years on an operating lease. This type of lease widely uses in business. It allows the business to use the equipment on a relatively short-term basis without purchasing it.
Special Consideration for operating lease:
The FASB amended its lease accounting standards on December 15, 2018, and they went into effect on that date. Most importantly, the norm now mandates that all leases be capitalized, with the exception of short-term leases of less than a year. The following are some of the other changes:
- Modifies the bright-line test to assist in determining whether a lessee has the authority to govern the specified asset.
- Installs a revised indirect cost definition, which will likely result in less indirect expenses being capitalized.
- In order for a sale or leaseback to take place, the asset must fulfill certain revenue recognition standards.
- Requires a significant number of new financial statement disclosures, both quantitative and qualitative, for both parties.
What qualifies as an Operating Lease?
The lease must fulfill certain conditions under generally accepted accounting principles in order to be categorized as an operational lease (GAAP).
- Lease payments are recognized as operational expenditures under an operating lease, just like they are in a rental.
- Leased assets are not recognized on the balance sheet of the firm; instead, they are expensed on the income statement. As a result, they have an impact on both operating and net profits.
- It is kept by the lessor for the duration of the lease and cannot include a bargain purchase option. The term is less than 75% of the asset’s projected economic life, and the lease payments’ present value (PV) is less than 90% of the asset’s fair market value.
What are the advantages of Operating Lease?
- When Equipment is Required for Short Duration:
When a business needs equipment for the short term, the operating lease can be considered as the best option. It also allows the business not to make a large investment in equipment for short-term use. The management can use the fund to generate more profitable opportunities.
- Equipment Might Become Outdated Quickly:
Operating a lease is beneficial when there is a risk of obsolescence. Due to technological advances and industry demand disruptions, your equipment may obsolete within few years. Short term lease may help to mitigate the risk.
- Restricted Cash Flow:
Operating a lease helps the business when the cash flow is tight. A business with a tight budget may avoid a substantial up-front charge. They can make payments from cash flow generated from the new equipment.
- Tax Benefits:
The most popular advantage of opportunity lease is the potential tax benefits. The lease payments of an operating lease can be deducted from the operating expenses during the lease period. It’s better to consult a tax advisor for which situation is most advantageous for your business.
Disadvantages of operating Lease:
- Finance Cost
There is an interest portion embedded in the lease payment/installment. In most cases, the rate of interest is higher than the prevailing market rate.
- Return for equity holders is reduced
In the operating lease, the business does not own the equipment. It is considered as a liability on the financial statement and eventually leads to a reduced return on equity for shareholders.
- No buildup in equity
When the business purchases some assets, it will increase the equity. In an operating lease, though the business is paying a good amount, in the end, it does not own the asset.
- Regular monthly payment
A lease is a commitment. The business must pay the monthly payments for the length of the contract.
How is a lease defined under IFRS lease accounting vs. GAAP?
GAAP and IFRS, the most widely accepted accounting standard defined the lease differently. In IFRS, all leases are considered as financial leases while GAAP standard differentiates between a finance lease and an operating lease.
Both forms of leases are required to have a right-of-use asset and a lease obligation on the balance sheet under the new FASB standard. In the case of a finance lease, however, interest on the lease obligation is recorded in the income statement independently from the amortization of the right-of-use asset.
In the case of an operational lease, the income statement shows a single lease expense that is usually distributed on a straight-line basis over the lease period.
Accounting Effect of Financial Lease and Operating lease
Prior to the recent accounting revisions, capital leases were reported on the lessee’s balance sheet as the asset’s starting value and the cumulative lease payments’ present value. Operating leases, on the other hand, were not recorded on the company’s balance sheet and were instead included in the financial statements’ footnotes. ‘Off-balance-sheet finance’ was the term for this.
Operating leases with periods of one year or longer must now be reported on the lessee’s balance sheet, pursuant to FASB regulation ASC842. This move will result in the company’s obligations increasing by more debt.
The rise in reported debt may have an influence on different debt financial ratios, as well as the company’s ability to qualify for further business credit alternatives.
When negotiating a lease, a small business owner should consult with a competent accountant to evaluate the impact on the company’s financial status.
What is the best choice: Financial Lease vs Operating Lease?
“It depends,” as is the case with many business choices.
A capital lease allows you to utilize an asset for a prolonged length of time before purchasing it for a lower price than its current market worth. This option is intriguing since it allows you to test it out before making a purchase. If you are dissatisfied with the rented asset, you may terminate the lease early and avoid the bother of selling it if you owned it. If you like the asset, you can use your right to acquire it at a reduced price.
A capital lease, on the other hand, exposes you to the hazards of ownership. You must pay for any repairs that the item requires.
You are renting the asset with an operating lease; you do not own it and do not have the opportunity to buy it for a low price. It is the obligation of the lessor to perform repairs if the item is in need of upkeep.
The interest component of a capital lease payment is tax-deductible, and it is represented on the balance sheet as a liability compared to a loan. In most situations, you may also deduct the annual depreciation of the leased item from your taxes, saving you money.
On the other hand, a capital lease exposes you to the risks of ownership. Any repairs that the item requires must be paid for by you.
You’re renting the asset through an operational lease; you don’t own it and don’t have the option to acquire it cheaply. If the object has to be maintained, it is the responsibility of the lessor to do so.
The interest portion of a capital lease payment is tax-deductible, and it is recorded as a liability on the balance sheet, similar to a loan. In most cases, you may deduct the leased item’s annual depreciation from your taxes, saving you money.
FAQ
How do you know if it’s a capital lease or an operating lease?
We can identify the capital lease or operating lease by the following factors:
- Transfer of ownership
- Bargain purchase option
- Lease term
- Present value
- Specialized nature
Is a capital lease an operating lease?
No, a capital lease is different from an operating lease. A capital lease is also known as a finance lease or sales lease. In a capital lease, the lessee pays rent in exchange for the right of ownership and at the end lease period, the lessee has the option to buy the asset. But, In an operating lease, the lessee pays the rental but has no option to buy.
Who gets depreciation in a capital lease?
The lessee entry a periodic depreciation charge to gradually reduce the amount of the fixed asset in the balance sheet.
Do you depreciate a capital lease?
A capital lease will be depreciated in the balance sheet of the lessee.
What is a lease vs rent?
A lease is a contract in which one party rents land, buildings, or other property from another party for a certain length of time; it is also a contract or document in which one party conveys property to another for a set period of time. You will find more about the lease agreement and rental agreement in this article.
On the contrary, Rent is a payment given to the owner of a property on a regular basis for the use of that property, as specified by a rental agreement.
Is capital lease an asset or liability?
A capital lease is considered the purchase of an asset for accounting purposes. It is recorded on the asset side of the balance sheet.
So, If you have any confusion or suggestion about the difference between finance lease and operating lease, you may comment below.
Feel to share with your friends!

